Keywords:
itolizumab, itolizumab’s R&D Progress, Mechanism of Action for itolizumab, drug target for itolizumab.
Description:
This article summarized the latest R&D progress of itolizumab, the Mechanism of Action for itolizumab, and the drug target R&D trends for itolizumab.
Text:
itolizumab‘s R&D Progress
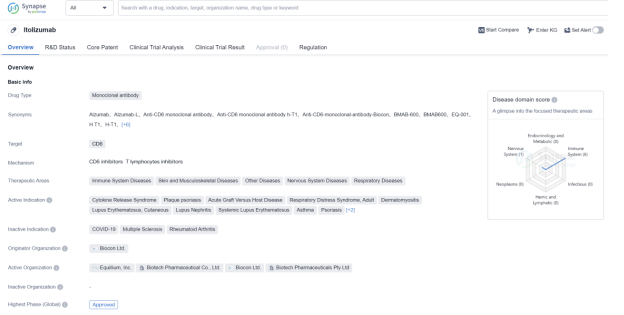
Itolizumab is a monoclonal antibody drug that targets CD6, a protein involved in immune system regulation. It is primarily used in the treatment of various immune system diseases, skin and musculoskeletal diseases, nervous system diseases, and respiratory diseases. The drug has been approved for use in several indications, including cytokine release syndrome, plaque psoriasis, acute graft versus host disease, respiratory distress syndrome in adults, dermatomyositis, lupus erythematosus, cutaneous lupus nephritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, asthma, and psoriasis.
The originator organization of Itolizumab is Biocon Ltd., a pharmaceutical company based in India. The drug received its first approval in India in January 2013. It is classified as an orphan drug, indicating that it is intended to treat rare diseases or conditions.
In terms of its development, Itolizumab has reached the highest phase of development which is approved globally. However, in China, it is currently in Phase 1, suggesting that it is still undergoing early-stage testing in that country.
Itolizumab’s approval and therapeutic areas highlight its potential in addressing a wide range of diseases and conditions related to the immune system, skin, musculoskeletal system, and respiratory system. Its targeting of CD6, a protein involved in immune system regulation, makes it a promising candidate for the treatment of various immune-related disorders.
Please click on the image below to directly access the latest data (R&D Status | Core Patent | Clinical Trial | Approval status in Global countries) of this drug.
Mechanism of Action for itolizumab: CD6 inhibitors Tlymphocytes inhibitors
CD6 inhibitors are a type of medication that specifically target and inhibit the activity of CD6, a protein found on the surface of T lymphocytes. T lymphocytes, also known as T cells, are a type of white blood cell that play a crucial role in the immune system’s response to infections and diseases.
From a biomedical perspective, CD6 inhibitors are designed to modulate the immune response by blocking the interaction between CD6 and its ligand, which is typically CD166. This interaction is important for the activation and proliferation of T cells. By inhibiting CD6, these inhibitors can potentially reduce the excessive immune response seen in certain autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis.
CD6 inhibitors can be considered as a specific subset of T lymphocyte inhibitors, as they specifically target the CD6 protein. T lymphocyte inhibitors, on the other hand, refer to a broader category of medications that can target various components or pathways involved in T cell activation and function. These inhibitors can be used in the treatment of autoimmune diseases, organ transplantation, and certain types of cancer.
In summary, CD6 inhibitors are a type of medication that selectively inhibit the activity of CD6, a protein found on T lymphocytes. They are used to modulate the immune response and can be beneficial in the treatment of autoimmune disorders and other conditions involving abnormal T cell activation.
Drug Target R&D Trends for itolizumab
CD6, also known as Cluster of Differentiation 6, is a cell surface glycoprotein that plays a crucial role in the human immune system. It is primarily expressed on T cells, a type of white blood cell involved in immune response. CD6 acts as a co-stimulatory molecule, enhancing T cell activation and proliferation. It also facilitates cell adhesion and interaction between T cells and antigen-presenting cells. CD6 has been implicated in various immune processes, including T cell development, differentiation, and regulation of immune responses. Understanding the role of CD6 can provide valuable insights into immune system function and potential therapeutic targets for immune-related disorders.
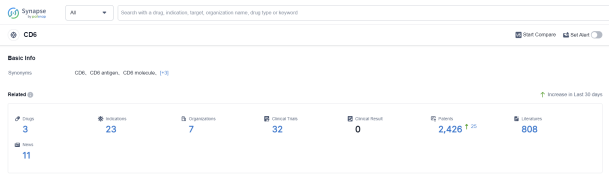
According to Patsnap Synapse, as of 6 Sep 2023, there are a total of 3 CD6 drugs worldwide, from 7 organizations, covering 23 indications, and conducting 32 clinical trials.
Based on the analysis of the provided data, the current competitive landscape of target CD6 in the pharmaceutical industry is characterized by the presence of multiple companies, including Biocon Ltd., Equillium, Inc., and Beijing Eastern Biotech Co Ltd, among others, actively involved in the development of drugs targeting CD6. The highest stage of development is the Approved phase, indicating successful advancements in clinical trials. The indications for these drugs cover a wide range of diseases and conditions, showcasing the potential therapeutic applications of target CD6. Monoclonal antibodies and Antibody toxin conjugates are the most rapidly progressing drug types, indicating intense competition in the market. Various countries/locations, including India, the United States, and Australia, are actively developing drugs targeting CD6. Further analysis is required to gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape and future development prospects of target CD6 in the pharmaceutical industry.Please click on the picture link below for free registration or log in directly if you have a freemium account, you can browse the latest research progress on drugs, indications, organizations, clinical trials, clinical results, and drug patents related to this target
Conclusion
Overall, Itolizumab’s approval, therapeutic areas, and target protein make it a valuable drug in the field of biomedicine. Its successful development and approval in multiple indications demonstrate its potential to provide effective treatment options for patients suffering from various immune-related diseases.